BIG FRIENDLY ROBOT DOG V1 / 2018
|
Short Description:
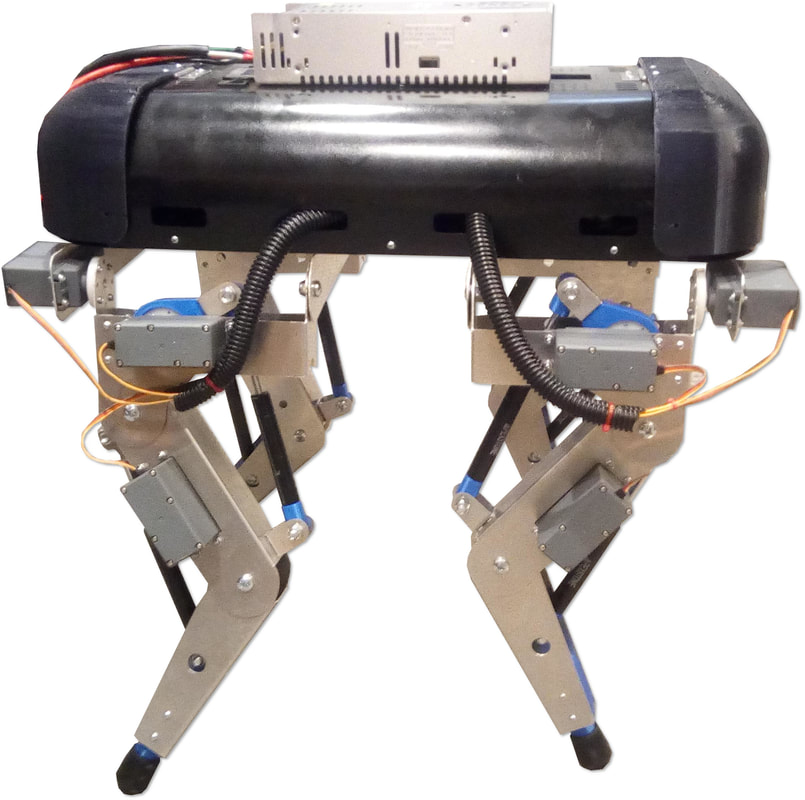
This big friendly robot dog (BFRD) is a 2.5-ft mid-sized quadrupedal robot dog built for the purpose of exploring four-legged walking dynamics. Longer Description: At 2.5-ft tall and 26 lbs, the BFRD V1 is roughly the size of an average mid-sized house dog. Heavily inspired by the Boston Dynamic's Big Dog and Spot Mini line of quadrupedal robots, this big friendly robot dog (BFRD V1) is an exploration of four legged walking dynamics. This robot's four legs that are articulated like an mammalian animal's, with heavy duty RC servo-motors combined with automotive gas springs acting as semi-compliant elements to absorb shock and recycle energy from one step to the next. The BFRD V1's on-board computer is an NVIDIA Jetson TX2 coupled with an Arduino Mega 2560, controlling locomotion, processes, sensors, and communications with the user. While not fully developed yet, in theory, the control system will keep the robot dog balanced, managing locomotion on a wide variety of terrain with real-time navigation. Walking robots are hard! Currently, balance and stability became hard to control as soon as one leg lifted up. We concluded that these current servo motors, though strong enough, were not fast enough to achieve an active walking motion without falling over. Also, At full load, the robot dog takes in 48-60 amps of continuous power at 5 volts. Creating a truly active walk like Boston Dynamics or MIT's Cheetah would require another leg redesign with even more powerful, high speed and precise motors. Further development would include adding advanced simultaneous locomotion and mapping with LIDAR sensors and significantly improving the motor setup. |
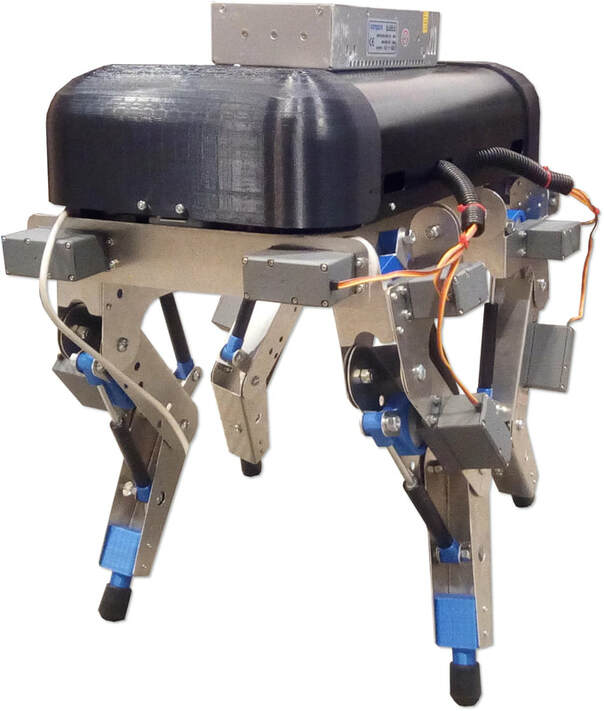
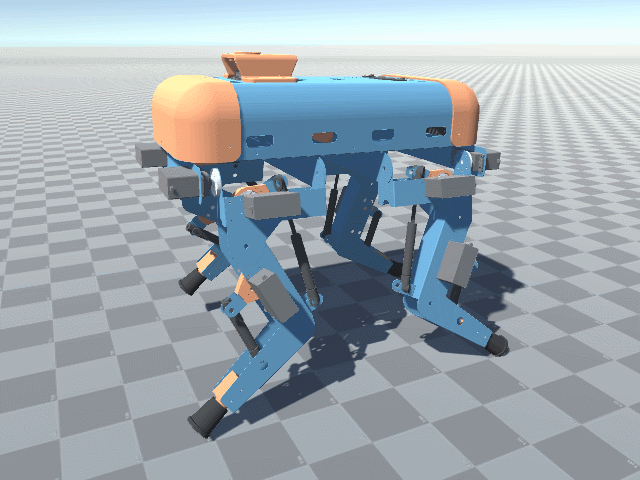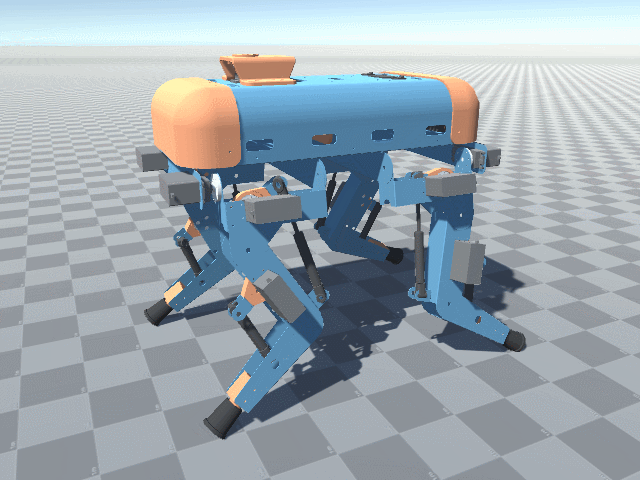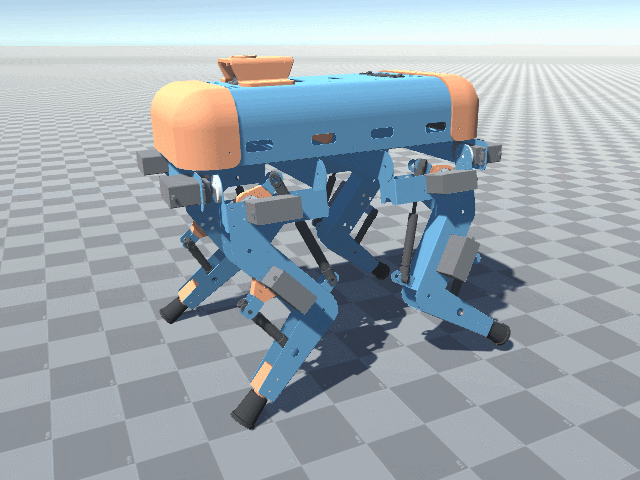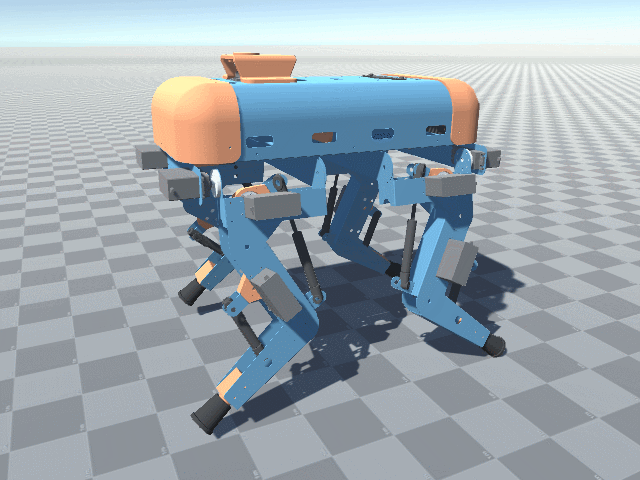
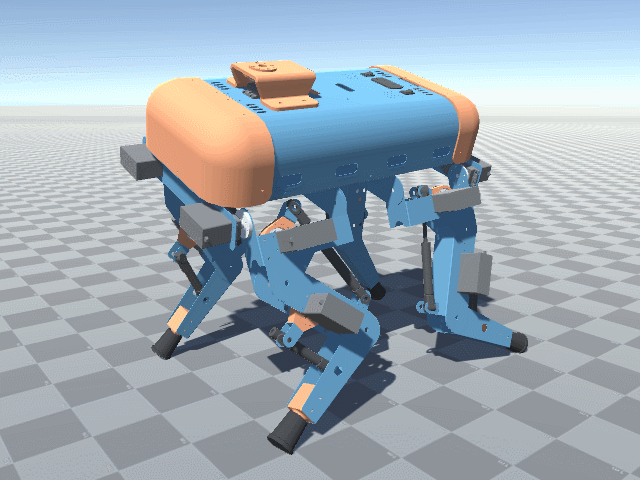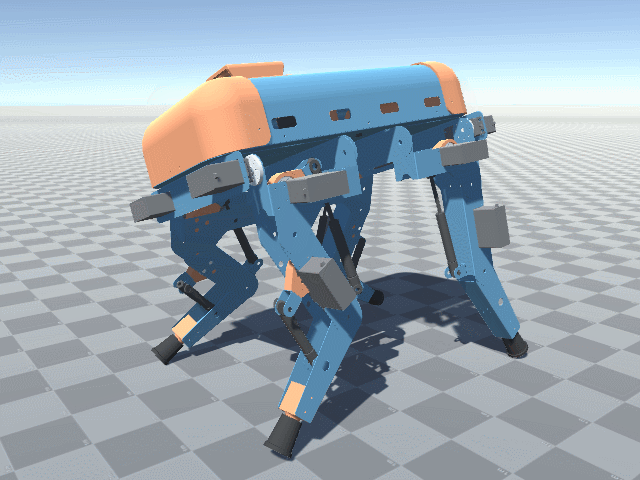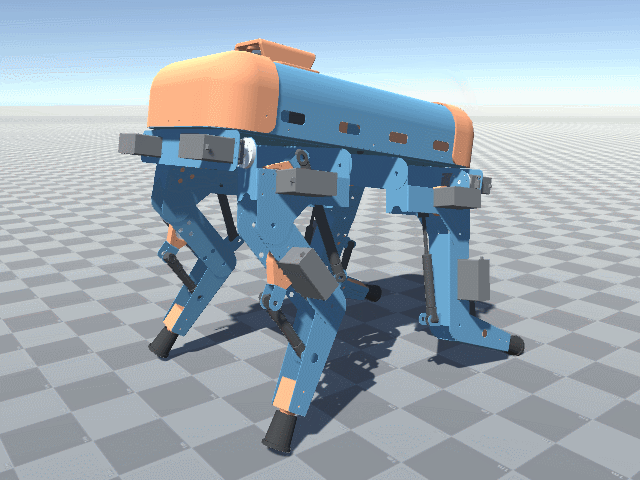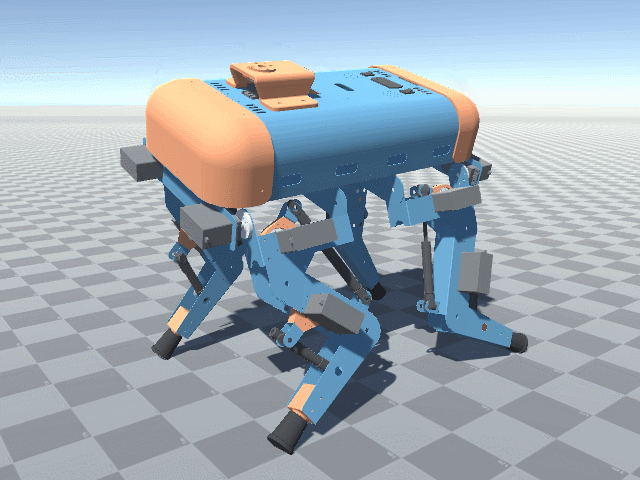
Frontal perspective view of Big Friendly Robot Dog V1. The robot has 12 heavy servo motors, and a big 5V 60A wired power supply, which can be swapped with batteries.
|
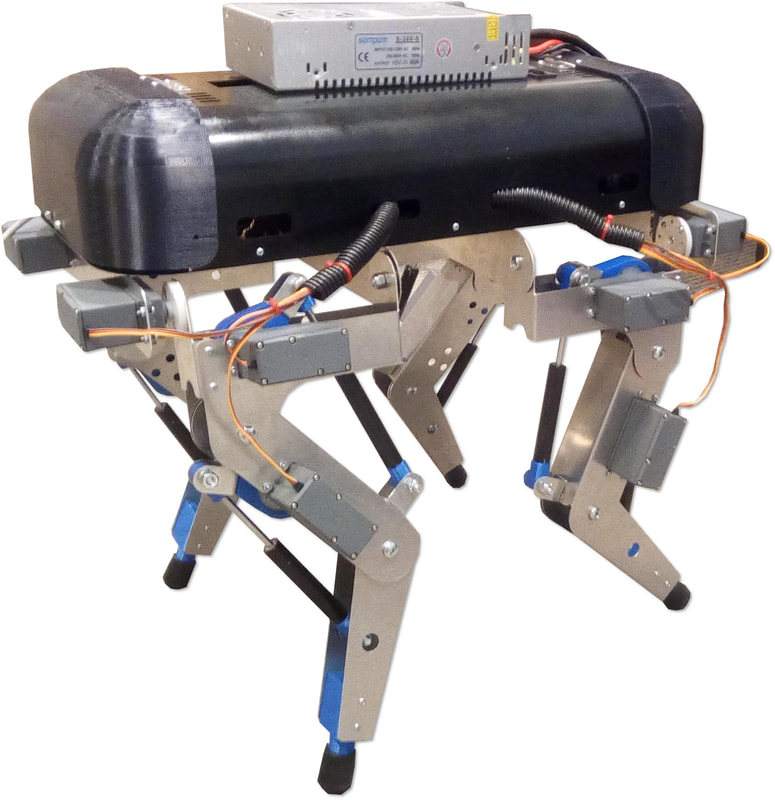
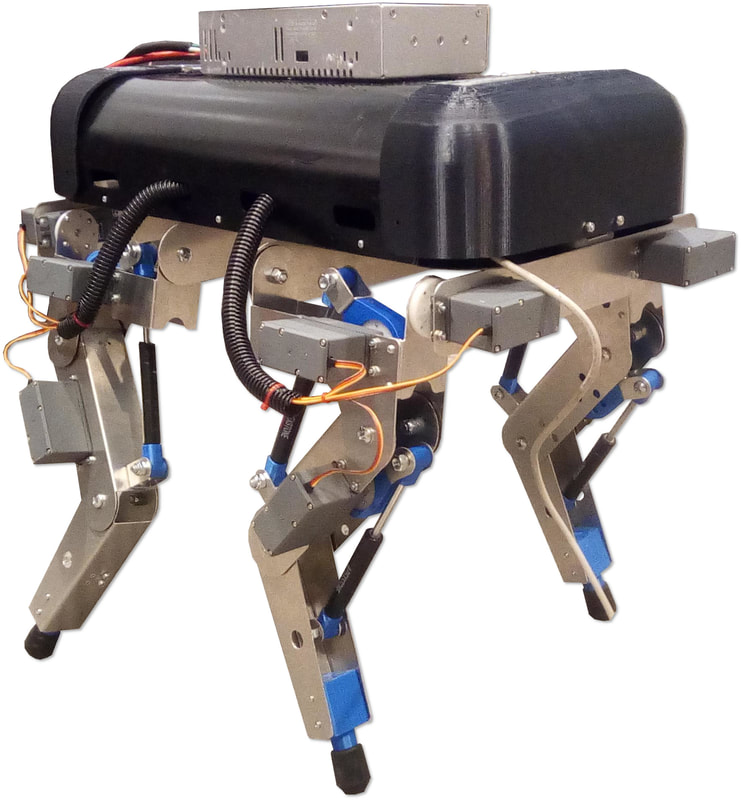
More angled perspective views of the Big Friendly Robot Dog V1.
|
|
Physics Simulator
A real-time quadrupedal physics enabled simulation was built in Unity to accurately show the dynamics of walking and joint motion and it's effect on the position, rotation, and inertia of the robot dog. A simple machine learning set was trained to calculate the optimal walking gait and timing of the robot dog to maximize stability and forward motion, which can be played in real time on the robot dog. |